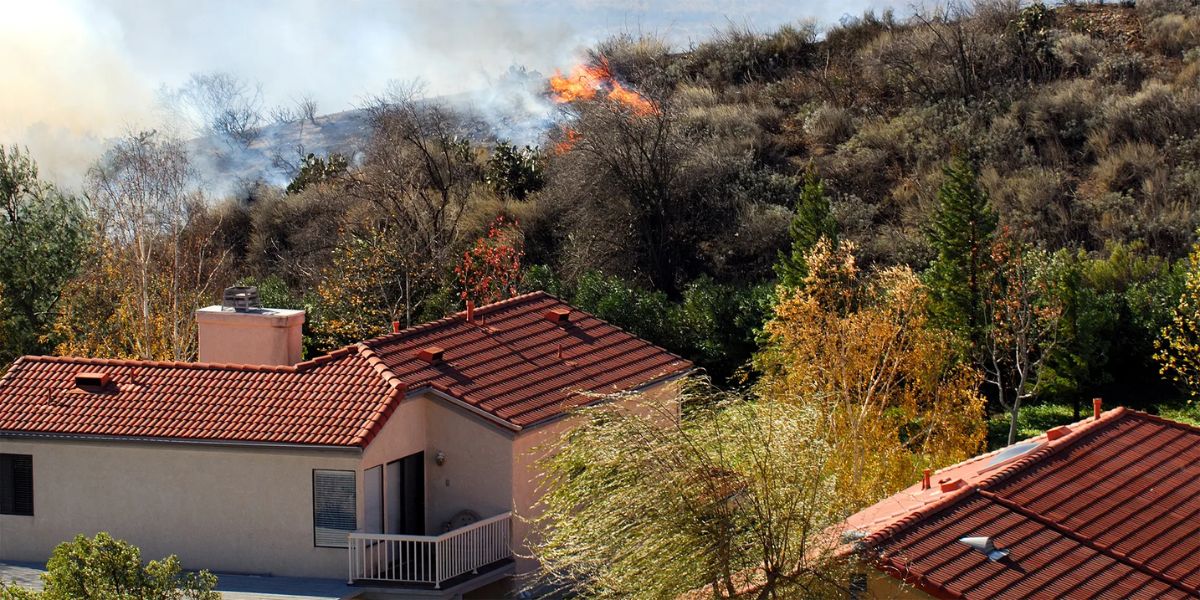
Creating a neighborhood emergency plan is an essential step in ensuring the safety and resilience of a community during times of crisis. In Los Angeles, where the risks of earthquakes, wildfires, and other natural disasters are prevalent, having a well-structured and legally compliant emergency plan is crucial. This article will walk you through the legal requirements for developing an effective neighborhood emergency plan in Los Angeles.
Understanding the Importance of a Neighborhood Emergency Plan
Before delving into the legalities, it’s important to recognize the critical role a neighborhood emergency plan plays. When disaster strikes, well-prepared neighborhoods can respond swiftly, minimizing loss of life and property. A community that is organized and ready can quickly help its residents evacuate, provide first aid, and establish emergency shelters.
Table of Contents
In Los Angeles, where diverse communities face varying degrees of vulnerability, a neighborhood emergency plan ensures that everyone, including families, seniors, and those with disabilities, is adequately supported.
Legal Framework for Emergency Planning in Los Angeles
Local Government Regulations
While creating a neighborhood emergency plan is not mandated by the state of California for individual neighborhoods, local regulations and guidelines strongly encourage it. Los Angeles City Emergency Management, under the Los Angeles Emergency Management Department (EMD), provides specific guidance on disaster preparedness and planning. The Los Angeles Municipal Code (LAMC) includes provisions that require property owners and residents to plan for hazards, including fire prevention and emergency evacuation routes.
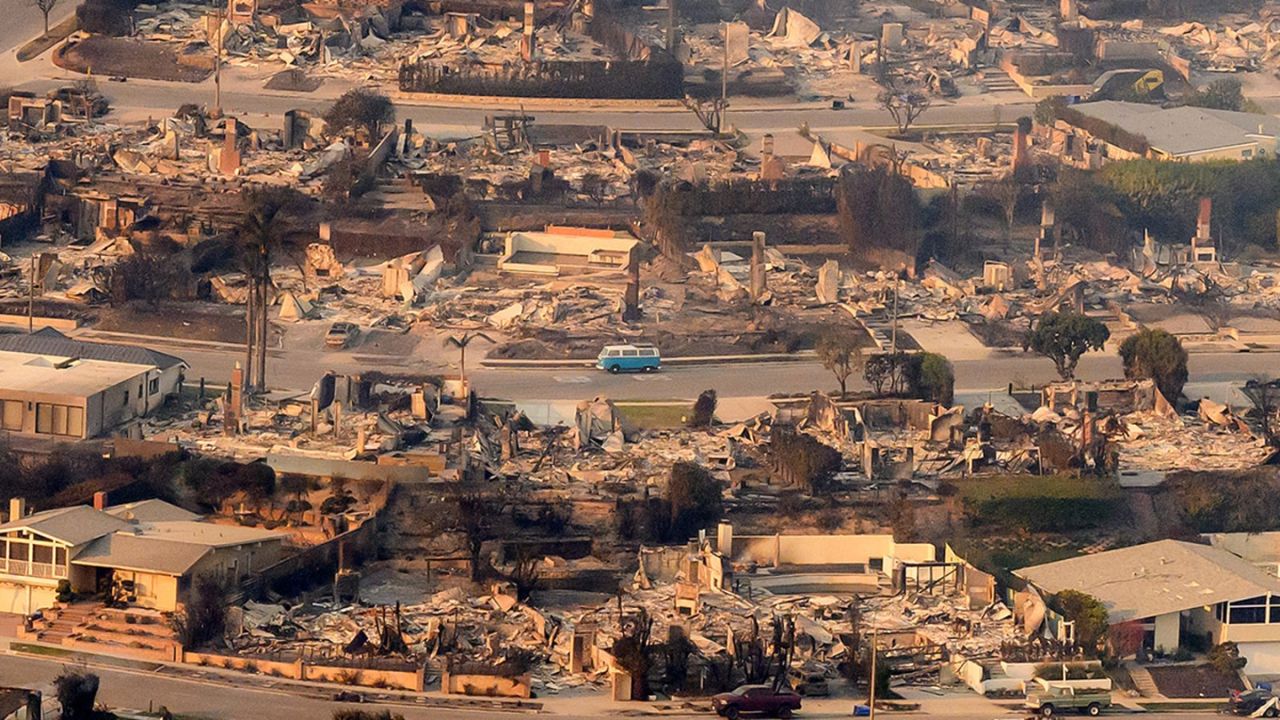
For example, the Los Angeles Fire Department (LAFD) has detailed requirements for residents living in high-risk areas like the foothills, especially regarding fire safety measures. These may include creating defensible space, having fire-resistant materials, and designing fire evacuation routes for neighborhoods prone to wildfires.
California State Requirements
California’s Emergency Services Act mandates that local governments have comprehensive emergency plans to protect public health and safety in the event of natural and man-made disasters. While this primarily applies to municipalities, the state encourages neighborhoods to integrate their plans into the broader community response framework.
In particular, the California State Hazard Mitigation Plan outlines requirements for local governments to engage communities in hazard reduction planning. Neighborhoods in Los Angeles are urged to create plans that align with these state guidelines to ensure a coordinated response to emergencies.
Key Legal Considerations for Your Neighborhood Emergency Plan
When developing a neighborhood emergency plan, certain legal considerations need to be addressed to ensure that the plan is both effective and compliant with local and state laws.
1. Zoning and Land Use Laws
Los Angeles neighborhoods are subject to specific zoning laws that impact how emergency plans are developed. For instance, some areas may have restrictions on evacuation routes, shelter placements, or the types of buildings that can be constructed in high-risk areas. It’s important for neighborhood planners to consider zoning laws and ensure that emergency access routes comply with local regulations.
2. Evacuation Routes and Access Points
Creating clear evacuation routes is essential for any neighborhood emergency plan. These routes must comply with local building and fire codes, which are enforced by the city and the Los Angeles Fire Department. The Los Angeles Fire Code requires specific measures for neighborhoods in fire-prone areas, including minimum width standards for evacuation routes and ensuring that streets are clear of obstructions.
Additionally, certain neighborhoods, especially those in the hills or on steep terrain, must account for road access and the ability for emergency vehicles to reach residents quickly. These legal requirements are not only critical for safety but are often enforced by local authorities during inspections.
3. Community Engagement and Public Participation
Under California law, local governments are encouraged to involve communities in disaster planning. The California Emergency Services Act emphasizes public participation in emergency planning, and the Los Angeles Office of Emergency Management (OEM) has implemented programs to facilitate community engagement.
Neighborhoods are encouraged to host public meetings, workshops, and training sessions where residents can learn about the emergency plan, provide feedback, and volunteer to assist in various capacities. This legal requirement ensures that all residents, including vulnerable populations, are included in emergency planning efforts.
4. Liability and Insurance Considerations
While neighborhoods are not required to provide insurance for individual properties during a disaster, homeowners and property owners may be required to carry insurance that covers disaster-related damages. When organizing a neighborhood emergency plan, it’s crucial to understand the liability and insurance implications, especially if the plan involves providing shelter or communal resources. Neighborhoods may need to consult with legal experts to ensure they are not exposed to unnecessary liability.
Steps for Creating a Legally Compliant Neighborhood Emergency Plan
1. Assess Local Risks
Begin by identifying the most likely risks in your neighborhood. Are you in an area prone to wildfires, earthquakes, flooding, or other hazards? Understanding these risks will help you tailor your emergency plan to address specific vulnerabilities.
2. Establish Key Roles and Responsibilities
Appoint a team of volunteers who can take leadership during emergencies. This includes individuals responsible for coordinating evacuations, providing first aid, and managing emergency shelters. Make sure the roles are clearly defined, and that all residents are informed about them.
3. Develop Clear Communication Strategies
Communication is essential during an emergency. Ensure that your neighborhood emergency plan includes clear communication methods, such as phone trees, social media groups, or text messaging systems. This will help keep all residents informed and connected during crises.
4. Prepare Your Evacuation Routes
Create and mark clear evacuation routes that comply with city regulations. Work with local fire departments or emergency services to ensure the routes are accessible and meet the necessary safety standards.
5. Conduct Regular Drills and Trainings
Once the plan is in place, hold regular drills to ensure everyone knows their role and can respond effectively when needed. Collaborate with local emergency responders to simulate real-life disaster scenarios and refine the plan as necessary.
Conclusion: Take Action for a Safer Community
A well-prepared neighborhood is a resilient one. By understanding and implementing the legal requirements for creating an emergency plan in Los Angeles, you ensure the safety and well-being of your community. As you develop your plan, remember that collaboration, legal compliance, and regular practice are key to success.
Get involved today! Start by gathering your neighbors for a planning session, consult with local authorities, and begin developing a legally sound emergency plan that will help protect your community when it matters most.