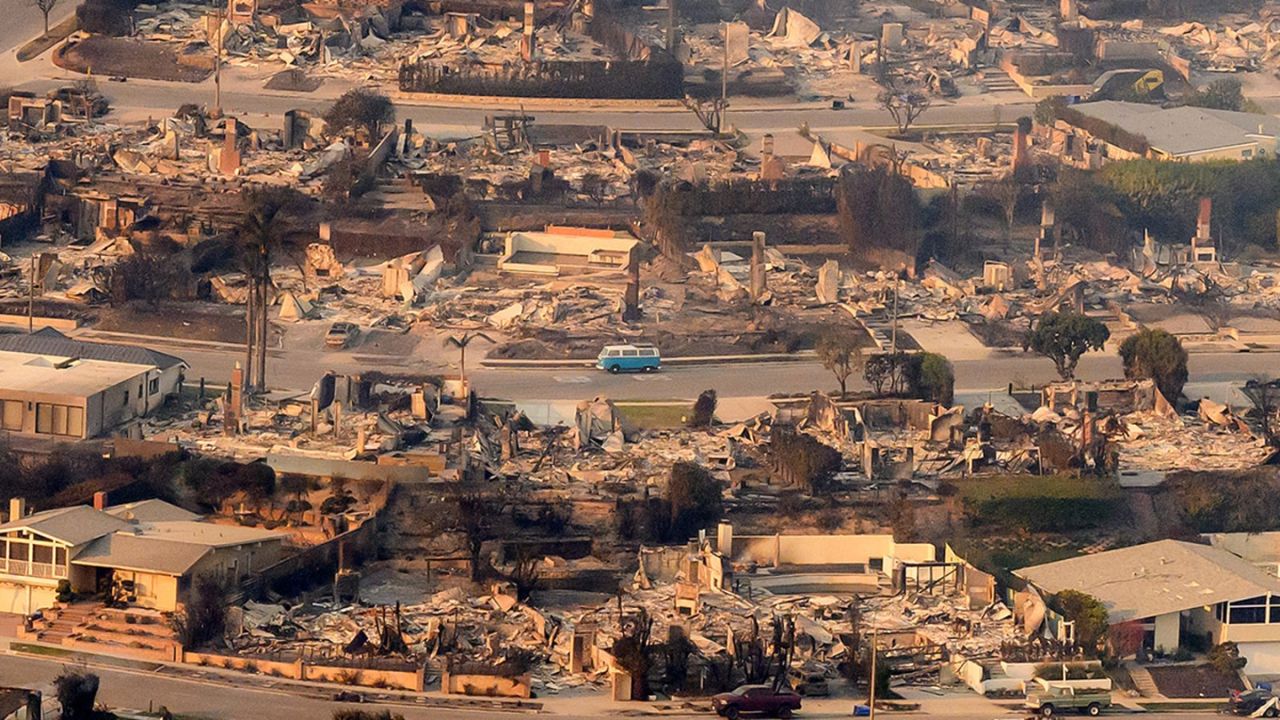
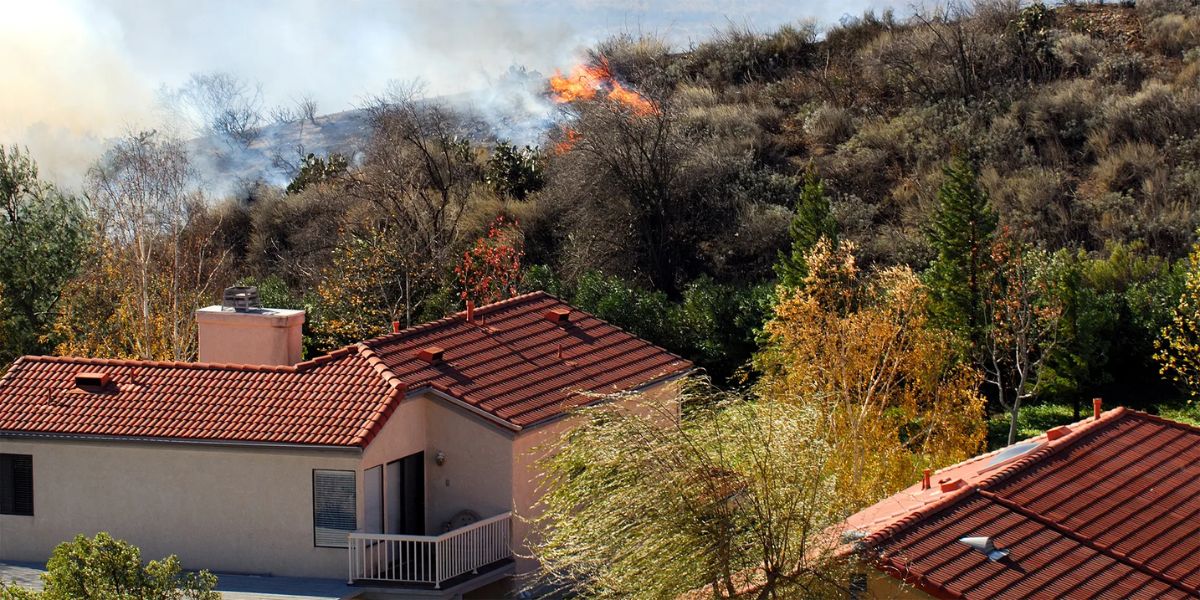
As hillside communities across Los Angeles County continue to face increasing wildfire threats, the importance of well-planned evacuation routes has never been greater. For residents living near canyons, foothills, or brush-heavy slopes, knowing how to leave safely during a fast-moving fire can mean the difference between security and chaos. Effective evacuation planning isn’t just about drawing lines on a map—it’s about understanding terrain, traffic patterns, and community coordination.
Why Evacuation Route Planning Matters
Wildfires in LA County move fast, often driven by Santa Ana winds that can change direction within minutes. When evacuation orders are issued, narrow hillside roads can become dangerously congested, trapping residents and first responders alike.
Table of Contents
An effective evacuation plan identifies primary and secondary routes, ensures they remain accessible year-round, and communicates them clearly to all residents. The Los Angeles County Fire Department recommends that communities update these plans annually to reflect new construction, vegetation changes, or infrastructure work.
Identifying Local Hazards and Vulnerabilities
Every hillside community faces unique challenges. Roads in Topanga Canyon, Malibu, and Altadena differ in gradient, lane width, and proximity to combustible vegetation. The first step in mapping evacuation routes is understanding the specific risks:
- Roadway bottlenecks where traffic could stall.
- Dead-end streets with no alternate exits.
- Overgrown brush or debris that could block visibility or escape.
- Bridges or culverts that might be compromised during a fire.
Mapping tools like Cal Fire’s Fire Hazard Severity Zone Viewer and LA County’s GIS mapping portal can help community planners visualize terrain risks and prioritize escape corridors.
Collaborating with Local Agencies
Evacuation planning is most effective when residents work with city planners, fire departments, and public works officials. Many neighborhoods in LA County now participate in Community Evacuation Planning Workshops, where local authorities and residents identify choke points, safe zones, and staging areas.
In 2024, the Los Angeles County Office of Emergency Management partnered with several hillside communities to pilot neighborhood-level evacuation maps. These maps included QR codes linking to live updates, helping residents stay informed during fast-changing emergencies.
Using Technology to Improve Mapping Accuracy
Modern mapping tools have transformed evacuation planning. Communities can now use GIS software, drone imagery, and open-source platforms like Google Earth to create real-time evacuation visuals.
A growing number of Los Angeles neighborhoods are integrating mobile alert systems into their evacuation plans. These systems—such as Alert LA County—send text and phone alerts with detailed route information based on a user’s location. Combined with neighborhood mapping, these tools ensure that residents receive accurate instructions when seconds count.
Designing for Real-World Conditions
Maps are only useful if they reflect reality. During the 2020 Bobcat Fire, many residents discovered that their designated routes were too narrow for two-way traffic or blocked by emergency vehicles. To prevent this, planners must consider:
- One-way evacuation flows to avoid collisions.
- Parking restrictions on critical streets during fire season.
- Clear signage marking evacuation exits and safe assembly areas.
- Alternate routes in case primary paths are compromised.
Regular maintenance of these routes—trimming overgrown brush, fixing cracked pavement, or removing obstacles—should be part of every community’s fire-season preparation checklist.
Educating Residents Through Drills
An evacuation map means little if residents don’t know how to use it. That’s why community drills are a key component of preparedness. Neighborhood councils across La Cañada Flintridge, Chatsworth, and Pacific Palisades have begun conducting mock evacuations to test travel times and identify problem zones.
As Maya Ortiz, an urban resilience planner specializing in wildfire mitigation, explains:
“Maps save lives only when people understand them. Regular drills give communities a chance to practice under realistic conditions—because in an emergency, panic is the biggest obstacle.”
These drills not only prepare residents but also give fire and police departments data to improve traffic control and communication strategies.
Integrating Evacuation Maps with Community Preparedness Plans
Mapping evacuation routes should never happen in isolation. It must be part of a broader neighborhood preparedness plan that includes emergency contact networks, family meeting points, and plans for vulnerable populations like seniors or residents with mobility challenges.
By integrating evacuation mapping with CERT programs, local neighborhood councils, and home hardening workshops, communities can create a holistic approach to wildfire resilience.
A Path Toward Safer Communities
For hillside residents of Los Angeles County, wildfire evacuation mapping is not just about drawing escape lines—it’s about collaboration, communication, and commitment. Each map reflects a shared promise: that neighbors will work together to ensure no one is left behind when disaster strikes.
Through consistent updates, technological innovation, and community drills, LA’s hillside neighborhoods can transform their vulnerabilities into strengths. The goal is clear: when the next fire burns, every resident should already know where to go, how to get there, and how to stay safe.
What steps has your neighborhood taken to improve its evacuation readiness? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below on BeReadyLA.org.