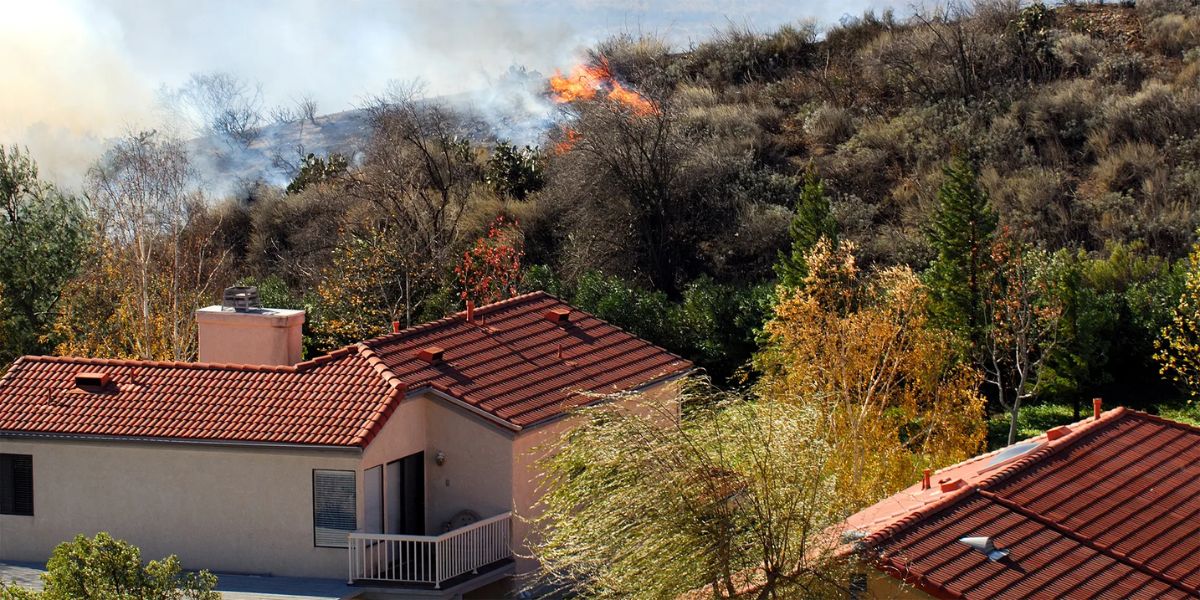
In Los Angeles, a city known for its diverse terrain and varying risks such as wildfires, earthquakes, and even floods, designing effective evacuation routes for neighborhoods is a crucial component of emergency preparedness. A well-planned evacuation route can save lives, reduce chaos, and ensure that residents can quickly and safely leave affected areas when disaster strikes. This article explores essential steps and best practices for designing evacuation routes that can make a real difference in LA’s neighborhoods.
Understanding the Risks and Challenges in LA
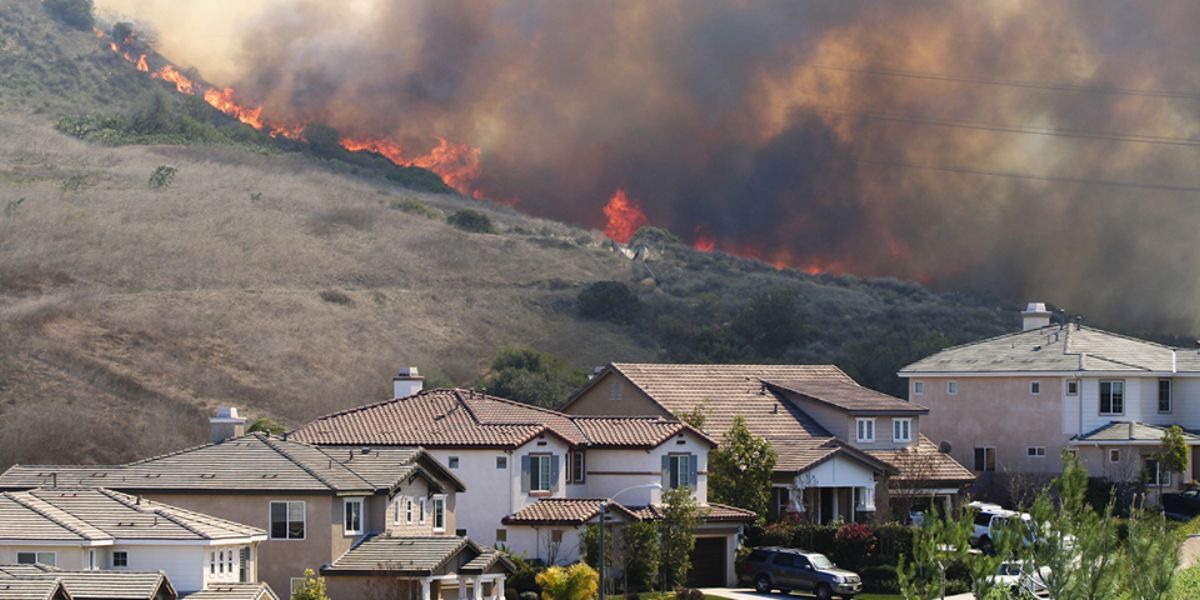
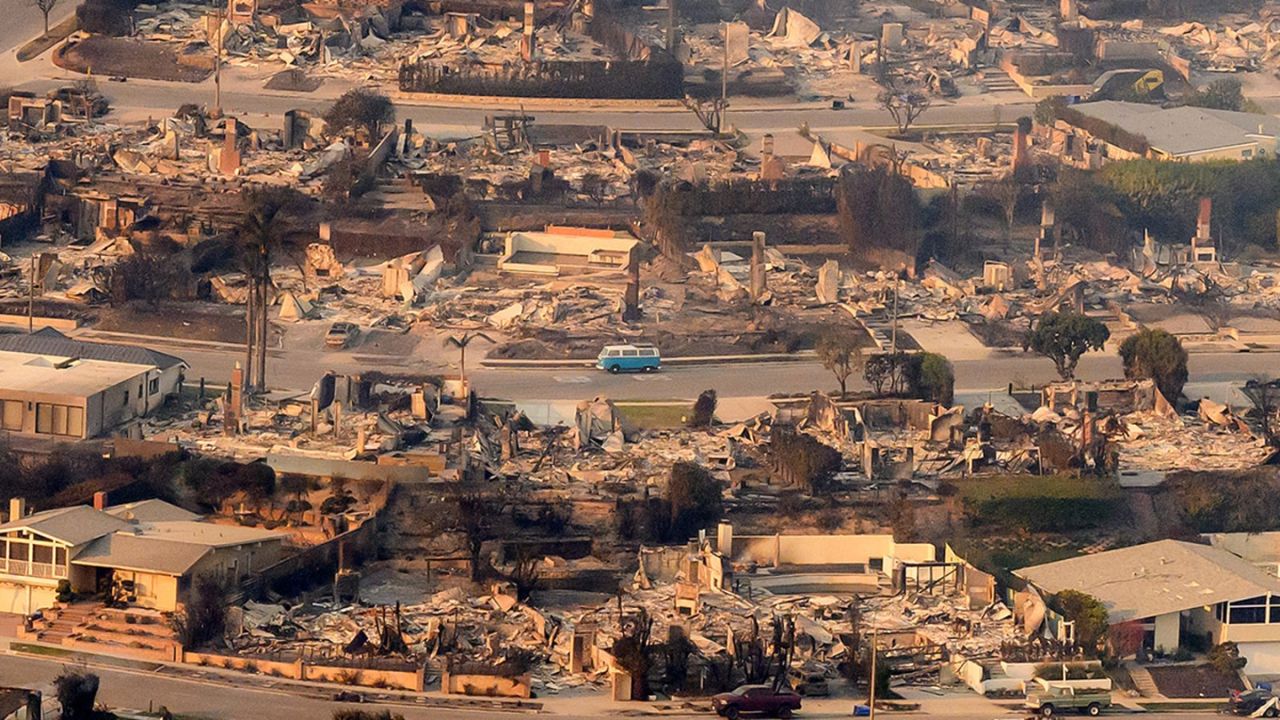
Los Angeles’ unique geography presents several challenges when designing evacuation routes. The city’s dense urban areas, coupled with its foothill and hillside communities, make navigating during an emergency difficult. Additionally, factors like limited access roads, traffic congestion, and infrastructure vulnerability due to natural disasters like wildfires and earthquakes need to be considered.
Table of Contents
Before designing an evacuation route, it is essential to evaluate the specific hazards that the neighborhood faces. A clear understanding of risks such as wildfires, earthquakes, and even man-made events, like civil unrest, is necessary to create an effective plan. By understanding the risks, emergency planners can develop evacuation routes tailored to the unique needs of each neighborhood.
Key Elements of an Effective Evacuation Route Plan
1. Multiple Evacuation Routes
One of the most important principles in evacuation planning is redundancy. Depending on one evacuation route can lead to traffic gridlock, especially during high-stress situations. LA neighborhoods should have multiple evacuation routes, each leading to different areas of refuge, like nearby highways, shelters, or safe zones.
It’s also vital to ensure that these routes are accessible to all residents, including people with disabilities, the elderly, and families with young children. Ensuring that the routes are adaptable to different types of emergencies (e.g., wildfires or earthquakes) will enhance the resilience of the community.
2. Clear Signage and Markings
Clear and visible signage is essential to guide people quickly and efficiently along evacuation routes. These signs should be designed to withstand extreme weather conditions and be easily visible at night. It’s crucial that all evacuation routes are marked with directional signs and distances to key locations like shelters, safe zones, and hospitals. Additionally, digital signs or apps that provide real-time updates during an emergency can be extremely helpful.
Proper signage can help reduce panic and confusion, especially in high-stress evacuation situations. Residents should also be informed about these evacuation routes beforehand through community outreach programs, local meetings, and informational materials.
3. Traffic Management and Control
LA’s neighborhoods often face traffic congestion, which can be a significant barrier during evacuation. To avoid bottlenecks and gridlocks, evacuation plans should incorporate strategies for traffic management. One effective strategy is to designate specific lanes for outbound traffic during emergencies, allowing evacuees to move more quickly.
Moreover, community planners should collaborate with local law enforcement and traffic departments to establish control points at key intersections. This ensures that traffic flows smoothly and that evacuees aren’t stuck in areas where roads are blocked or unsafe. It also helps prevent vehicles from taking unnecessary detours, saving valuable time during an evacuation.
4. Community Education and Drills
Designing an evacuation route is not enough if residents don’t know how to use it. It’s essential to conduct regular community drills to familiarize residents with the evacuation routes and emergency procedures. These drills should simulate real emergency scenarios such as wildfires or earthquakes and include evacuation procedures, emergency kit preparation, and transportation options.
Education about evacuation routes should be included in neighborhood meetings, local newsletters, and digital platforms, ensuring that everyone is on the same page. The more familiar residents are with the routes and procedures, the more confident and calm they will be when an emergency occurs.
5. Consideration of Vulnerable Populations
Special attention must be given to vulnerable populations, including the elderly, people with disabilities, children, and pets. Ensuring that evacuation routes are accessible to everyone is essential in any neighborhood evacuation plan.
Accessible transportation options should be included in evacuation planning for those who cannot drive, and these routes should be clear of obstacles. Furthermore, designated meeting points for vulnerable residents, such as seniors or those with mobility impairments, can help emergency responders efficiently locate and assist them during evacuations.
6. Evacuation Shelters and Safe Zones
Effective evacuation routes lead to safe shelters where people can find refuge during a disaster. Shelters should be clearly marked and equipped with resources like food, water, medical supplies, and communication tools. It’s essential to know the locations of these shelters ahead of time and plan evacuation routes that lead directly to them.
In addition to official shelters, pre-designated safe zones in the neighborhood can provide temporary refuge before evacuees are directed to more permanent shelters. These zones should be located away from immediate threats, such as areas prone to flooding or wildfires.
The Role of Technology in Evacuation Planning
Incorporating technology into evacuation planning can significantly enhance its effectiveness. Tools like mobile apps, social media, and digital maps can be used to keep residents informed in real-time. For example, an app can provide notifications about road closures, changes to evacuation routes, or the status of nearby shelters.
Another helpful tool is geographic information system (GIS) technology, which allows planners to create detailed maps of evacuation routes, identify the most vulnerable areas, and simulate the flow of traffic during an evacuation. These tools provide valuable insights that can be used to improve and refine evacuation strategies.
Conclusion
Designing effective evacuation routes for LA neighborhoods is a complex but necessary task. By considering the unique challenges of the city’s geography, the needs of vulnerable populations, and the importance of clear communication and traffic management, communities can ensure that their evacuation routes are efficient, safe, and effective.
If you’re a Los Angeles resident, take the time to familiarize yourself with your neighborhood’s evacuation routes. Work with your local neighborhood council to improve and update evacuation plans. Together, we can build a safer, more resilient LA. Visit bereadyla.org for more resources and information on emergency preparedness.